Navigating the Layers of the Internet: Unveiling the Surface, Deep, and Dark Web
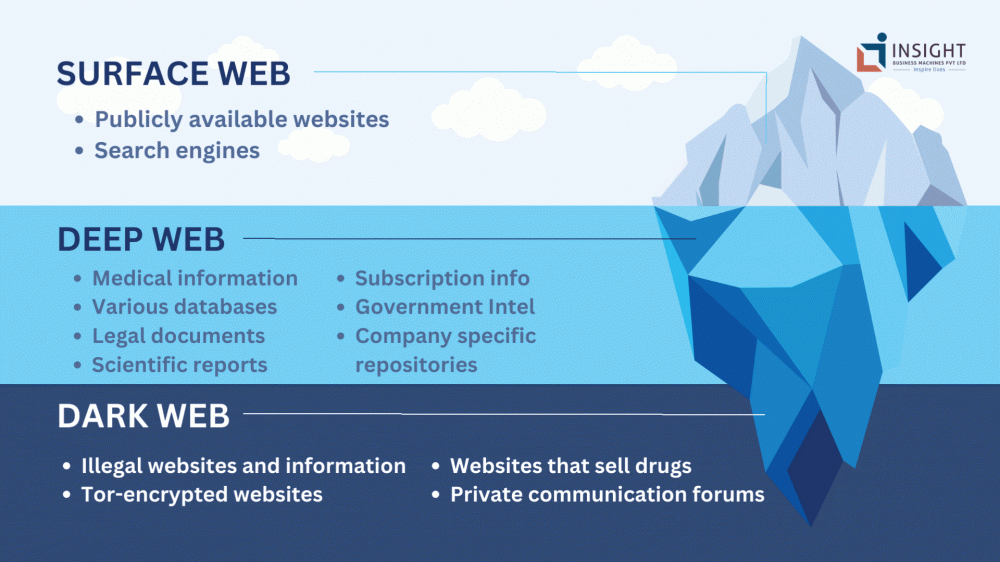
ArticleSurface Web: The surface web, also known as the visible web or open web, is the portion of the internet that is indexed by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. It consists of websites and web pages that are accessible using standard web browsers without any special tools or authentication. This is where most of our everyday online activities take place.
Characteristics and Examples of the Surface Web:
Accessibility: Websites on the surface web are easily discoverable through search engine queries and can be accessed using common web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari.
Content: Publicly available information such as news articles, e-commerce platforms (Amazon, eBay), social media (Facebook, Twitter), informational sites (Wikipedia), and blogs are part of the surface web.
Indexing: Search engines use automated bots to crawl and index these websites, making them readily accessible to anyone.
Deep Web: The deep web refers to the portion of the internet that is not indexed by search engines. It includes websites and content that are hidden behind password protection, paywalls, or other security measures. Accessing the deep web requires specific credentials or knowledge, and it encompasses a vast amount of data beyond what's visible on the surface.
Characteristics and Examples of the Deep Web:
Inaccessible by Search Engines: Content in the deep web is not indexed by search engines, making it invisible to traditional search queries.
Private Data: Private databases, email accounts, online banking portals, subscription-based content (academic journals, premium news sites), and internal company resources are examples of deep web content.
Restricted Access: Users need login credentials, membership access, or specific URLs to access content within the deep web.
Dark Web: The dark web is a small but distinct portion of the deep web that is intentionally hidden and requires specialized software, such as the Tor browser, to access. It is known for its anonymity and encrypted communication, but it's also associated with illegal activities and criminal marketplaces.
Characteristics and Examples of the Dark Web:
Anonymity and Encryption: The dark web offers high levels of anonymity by routing traffic through multiple nodes and using encryption, making it difficult to trace users.
“. onion" Domains: Websites on the dark web often have addresses ending in “. onion" instead of traditional domains. Examples range from legal forums for free speech to illegal marketplaces selling drugs, hacking tools, and stolen data.
Mixed Content: While some content on the dark web is legal and privacy-focused, it also hosts illegal activities, such as drug trafficking, counterfeit money, and cybercrime services.
In summary, the surface web is what we commonly use and access daily, the deep web consists of content that's hidden behind passwords and paywalls, and the dark web is a secretive part of the deep web accessed through special tools, known for its anonymity and mixed legal and illegal content.